Friday, 31 May 2013
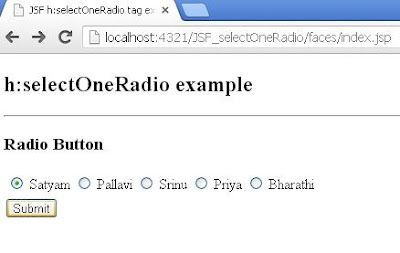
JSF selectOneRadio tag example
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
package com.satyamsoft;
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
JSF selectBooleanCheckbox tag example
1). JSF selectBooleanCheckbox tag Program Structure:
2). index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<%@taglib prefix="f" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"%>
<%@taglib prefix="h" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>JSF selectBooleanCheckbox tag example!</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function selectBooleanCheckbox(){
alert(document.getElementById('jsfselectBooleanCheckbox:chkRememberMe').checked);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<f:view>
<h1>JSF h:selectBooleanCheckbox tag </h1>
<h:form id="jsfselectBooleanCheckbox">
<h:selectBooleanCheckbox value="Remember Me" id="chkRememberMe" />
<h:commandButton value="Show Checked" onclick="selectBooleanCheckbox()" />
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>
3). OutPut
JSF inputHidden tag example
1). JSF inputHidden tag Program Structure:
2). index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<%@taglib prefix="f" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"%>
<%@taglib prefix="h" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>JSF inputHidden tag example!</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function showHiddenValue(){
alert(document.getElementById('jsfinputHiddenForm:hiddenField').value);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<f:view>
<h1>JSF h:inputHidden tag </h1>
<h:form id="jsfinputHiddenForm">
<h3>Get value from inputHidden field</h3>
<h:inputHidden value="Hello JSF World" id="hiddenField" />
<h:commandButton value="Click me to show Hidden Value" onclick="showHiddenValue()" />
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>
3). OutPut
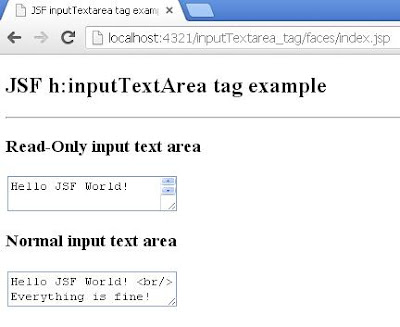
JSF inputTextarea tag example
1). JSF inputTextarea tag Program Structure:
2). index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<%@taglib prefix="f" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"%>
<%@taglib prefix="h" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>JSF inputTextarea tag example!</title>
</head>
<body>
<f:view>
<h2>JSF h:inputTextArea tag example</h2>
<hr/>
<h:form>
<h3>Read-Only input text area</h3>
<h:inputTextarea value="Hello JSF World!
<br/> Everything is fine!" readonly="true"/>
<h3>Normal input text area</h3>
<h:inputTextarea value="Hello JSF World! <br/> Everything is fine!"/>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>
3). OutPut
Tuesday, 28 May 2013
JSF DataTable
JSF provides a rich control named DataTable to render and format html tables.
- DataTable can iterate over collection or array of values to display data.
- DataTable provides attributes to modify its data in easy way.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" </html>Following are important DataTable operations in JSF 2.0:
S.No
|
Tag & Description
|
1
|
Display DataTable
How to display a datatable
|
2
|
Add data
How to add a new
row in a datatable
|
3
|
Edit data
How to edit a row in
a datatable
|
4
|
Delete data
How to delete a row
in datatable
|
5
|
Using DataModel
Use DataModel to
display row numbers in a datatable
|
JSF Validator Tags
JSF provides inbuilt validators to validate its UI components. These tags can validates length of field, type of input which can be a custom object.
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets" >
Following are important Validator Tags in JSF 2.0:
S.No
|
Tag & Description
|
1
|
f:validateLength
Validates length of
a string
|
2
|
f:validateLongRange
Validates range of
numeric value
|
3
|
f:validateDoubleRange
Validates range of float
value
|
4
|
f:validateRegex
Validate JSF
component with a given regular expression
|
5
|
Custom Validator
Creating a custom validator
|
Monday, 27 May 2013
JSF Convertor tags
JSF provides inbuilt convertors to convert its UI component's data to
object used in a managed bean and vice versa.For example, these tags
can convert a text into date object and can validate the format of input
as well.
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets" >
Following are important Convertor Tags in JSF 2.0:
|
S.No
|
Tag & Description
|
|
1
|
f:convertNumber
Converts a String
into a Number of desired format
|
|
2
|
f:convertDateTime
Converts a String
into a Date of desired format
|
|
3
|
Custom Convertor
Creating a custom convertor
|
JSF Facelets Tags
JSF provides special tags to create common layout for a web
application called facelets tags. These tags gives flexibility to manage
common parts of a multiple pages at one place.
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
Following are important Facelets Tags in JSF 2.0:
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets" >
Following are important Facelets Tags in JSF 2.0:
|
S. No
|
Tag &
Description
|
|
1
|
Templates
We'll demonstrate how to use templates using following tags
·
<ui:insert>
·
<ui:define>
·
<ui:include>
·
<ui:define>
|
|
2
|
Parameters
We'll demonstrate how to pass parameters to a template file using following tag
·
<ui:param>
|
|
3
|
Custom
We'll demonstrate how to create custom tags |
|
4
|
Remove
We'll demonstrate capability to remove JSF code from generated HTML page |
JSF Basic tags
JSF provides a standard HTML tag library. These tags get rendered into corresponding html output.
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
Following are important Basic Tags in JSF 2.0:
For these tags you need to use the following namespaces of URI in html node.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" >
Following are important Basic Tags in JSF 2.0:
|
S.No
|
Tag name
|
Description
|
|
1
|
h:inputText
|
Renders
a HTML input of type="text", text box.
|
|
2
|
h:inputSecret
|
Renders
a HTML input of type="password", text box
|
|
3
|
h:inputTextarea
|
Renders
a HTML textarea field.
|
|
4
|
h:inputHidden
|
Renders
a HTML input of type="hidden".
|
|
5
|
h:selectBooleanCheckbox
|
Renders
a single HTML check box.
|
|
6
|
h:selectManyCheckbox
|
Renders
a group of HTML check boxes
|
|
7
|
h:selectOneRadio
|
Renders
a single HTML radio button
|
|
8
|
h:selectOneListbox
|
Renders
a HTML single list box.
|
|
9
|
h:selectManyListbox
|
Renders
a HTML multiple list box.
|
|
10
|
h:selectOneMenu
|
Renders
a HTML combo box.
|
|
11
|
h:outputText
|
Renders
a HTML text.
|
|
12
|
h:outputFormat
|
Renders
a HTML text. It accepts parameters.
|
|
13
|
h:graphicImage
|
Renders
an image.
|
|
14
|
h:outputStylesheet
|
Includes
a CSS style sheet in HTML output.
|
|
15
|
h:outputScript
|
Includes
a script in HTML output.
|
|
16
|
h:commandButton
|
Renders
a HTML input of type="submit" button.
|
|
17
|
h:Link
|
Renders
a HTML anchor.
|
|
18
|
h:commandLink
|
Renders
a HTML anchor
|
|
19
|
h:outputLink
|
Renders a
HTML anchor.
|
|
20
|
h:panelGrid
|
Renders
an HTML Table in form of grid.
|
|
21
|
h:message
|
Renders
message for a JSF UI Component.
|
|
22
|
h:messages
|
Renders
all message for JSF UI Components
|
|
23
|
f:param
|
Pass
parameters to JSF UI Component.
|
|
24
|
f:attribute
|
Pass
attribute to a JSF UI Component.
|
|
25
|
f:setPropertyActionListener
|
Sets
value of a managed bean's property
|
Wednesday, 22 May 2013
JSF Life Cycle
JSF application lifecycle consist of six phases which are as follows
- Restore view phase
- Apply request values phase; process events
- Process validations phase; process events
- Update model values phase; process events
- Invoke application phase; process events
- Render response phase
The six phases show the order in which JSF processes a form. The list shows the phases in their likely order of execution with event processing at each phase.
Restore view
JSF begins the restore view phase as soon as a link or a button is clicked and JSF receives a request.During this phase, the JSF builds the view, wires event handlers and validators to UI components and saves the view in the FacesContext instance. The FacesContext instance will now contains all the information required to process a request.
Apply request values
After the component tree is created/restored, each component in component tree uses decode method to extract its new value from the request parameters. Component stores this value. If the conversion fails, an error message is generated and queued on FacesContext. This message will be displayed during the render response phase, along with any validation errors.If any decode methods / event listeners called renderResponse on the current FacesContext instance, the JSF moves to the render response phase.
Process validation
During this phase, the JSF processes all validators registered on component tree. It examines the component attribute rules for the validation and compares these rules to the local value stored for the component.If the local value is invalid, the JSF adds an error message to the FacesContext instance, and the life cycle advances to the render response phase and display the same page again with the error message.
Update model values
After the JSF checks that the data is valid, it walks over the component tree and set the corresponding server-side object properties to the components' local values. The JSF will update the bean properties corresponding to input component's value attribute.If any updateModels methods called renderResponse on the current FacesContext instance, the JSF moves to the render response phase.
Invoke application
During this phase, the JSF handles any application-level events, such as submitting a form / linking to another page.Render response
During this phase, the JSF asks container/application server to render the page if the application is using JSP pages. For initial request, the components represented on the page will be added to the component tree as the JSP container executes the page. If this is not an initial request, the component tree is already built so components need not to be added again. In either case, the components will render themselves as the JSP container/Application server traverses the tags in the page.After the content of the view is rendered, the response state is saved so that subsequent requests can access it and it is available to the restore view phase.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)